Innovations in care of newborn infants covering a range of conditions and treatments, signals a better life-start and improved health for future Americans. Neo-natal specialists avoid premature birth, seriously affecting 10% of infants, as it may cause mental and physical disabilities.

Research is being done on genetic and environmental influences on the fetus, such as a mother’s obesity, toxic substances exposure, etc. and better postpartum care for mothers and infants. Health improvement during pregnancy and infancy affects life-long health. Pediatric research provides insights into adult diseases and early health interventions prior to onset of chronic /aging diseases, can impact public health to ensure future savings.
Preventing preterm birth
A major cause of infant death is preterm birth, with survivors facing serious health challenges due to obesity, high blood pressure, heart disease and stroke, much later in life, if born between 28 to 32 weeks. Six pre-mature birth research centers are identifying causes of premature birth and its prevention. Predicting premature birth for women at highest risk is only 20% correct. Researchers have a new blood test for pregnant women with 75% to 80% accuracy, which tells whether a baby will be born prematurely, reliably and is less expensive than ultrasound.
The new blood test identifies a few genes in the mother’s placenta and fetus to provide reliable signals about gestational age and prematurity risk as the mother’s immune system, balancing threats to the mother and fetus. Rates of premature birth (delivery < 37 weeks’ gestation) declined steadily from 2007 to 2014, but increased in 2015 and 2016 and researchers are studying the environment role, prenatal care and genetic issues. Air Pollutants and agricultural pesticides enhance preterm-birth risk and exposures can be reduced for expecting mothers.
Risk Reduction to the Infant Brain
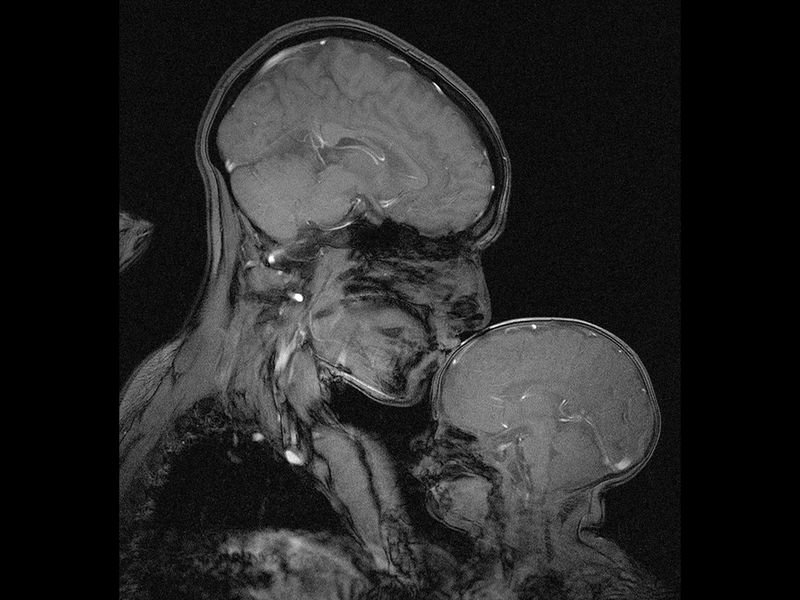
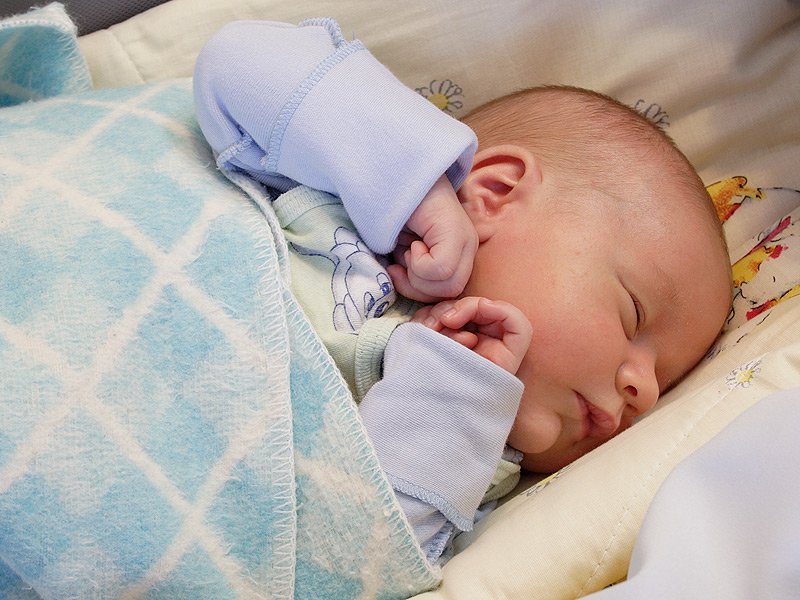
During delivery, full-term babies can risk brain injury if oxygen and blood supply are compromised. Reduced oxygen causes seizures, and infants with brain injury can develop cerebral palsy and developmental problems; issues reduced somewhat by therapeutic hypothermia or brain cooling treatment. The Embrace neo-natal MRI is a system designed to track how infants’ brains are developing, assess brain injury extent and guide which treatments prevent disability.
Infant genomes study
A “heel stick” blood test for newborns, screen about 30 conditions impacting a baby’s health, such as galactosemia preventing digestion of sugar in milk. Researchers need extensive screening of genome sequencing to examine large numbers of genes within the DNA of such infants. 325 families (randomized to receive sequencing or usual care) are studied for the first year of the baby’s life and fill out surveys about how the results play a role, till the child is 18. Sequencing at birth provides a template to predict conditions, decide medicines for an entire lifetime.
Epigenetics (external modifications to DNA that switch genes on and off) are useful in the study of the inheritance of traits such as obesity. In the U.S. > 60% of women are overweight at conception and more than one-third are obese, possibly predispose their infants to obesity, heart disease, and diabetes later in life. Weight-control genes may switch from obese to lean by dietary supplements, stress minimization or drug therapy. The epigenome after birth can be changed, by diet and exercise.
Low-tech breathing aids
Hospitals delay cutting the umbilical cord for up to a minute, a practice known as delayed cord clamping, to provide extra blood and nutrients from the placenta before detaching the infant from mother. Annually, 10 million babies are born not breathing with six million of those, needing resuscitation. In such cases, the cord is cut immediately and the babies handed over to the special resuscitation team. This low-tech, low-cost solution helps infants world-wide.
Umbilical catheters inserted through exposed blood vessels commonly secured with non-sterile tape, provide medication to newborns and cause bloodstream infections, contributing to poor growth and impaired brain development with increased hospital stays and costs for parents. Hospitals adopt rigorous protocols to reduce such infections, and researchers continue to look for prevention strategies.
Improving postpartum care
Maternal-health experts have a “fourth trimester concept” following birth, a critical period for a mother and infant for long-term health and well-being.
In May 2018, a Task Force recommended a number of improvements in traditional postpartum care (six weeks after delivery) with 40% of women not attending as visits ignore critical issues like emotional well-being, physical complications after birth, exercise, nutrition, sleep and fatigue. Counseling on breast-feeding issues or assessing a mother’s comfort while rearing the infant, are ignored.
Different Perspectives
The Task Force advocates reimbursement covering postpartum care as a continuing process and assessment of new mothers within three weeks after birth and ongoing care which concludes with a comprehensive visit, covering physical, social and psychological issues within 12 weeks of postpartum.
Paid parental leave is essential to enable women to recover after birth and nurture their infants requiring intense, womblike nurturing of the mother and infant as mutually dependent. U.S. is the only high-income country without paid maternity leave and 25% employed women return to work within two weeks after giving birth, long before recovery from childbirth.
A University of North Carolina website and other resources for postpartum supported by the Global Health Foundation, helps new mothers cope with physical, emotional, financial and relationship changes after having a baby.